Analysing the impacts of Russia's invasion of Ukraine on energy markets and energy security
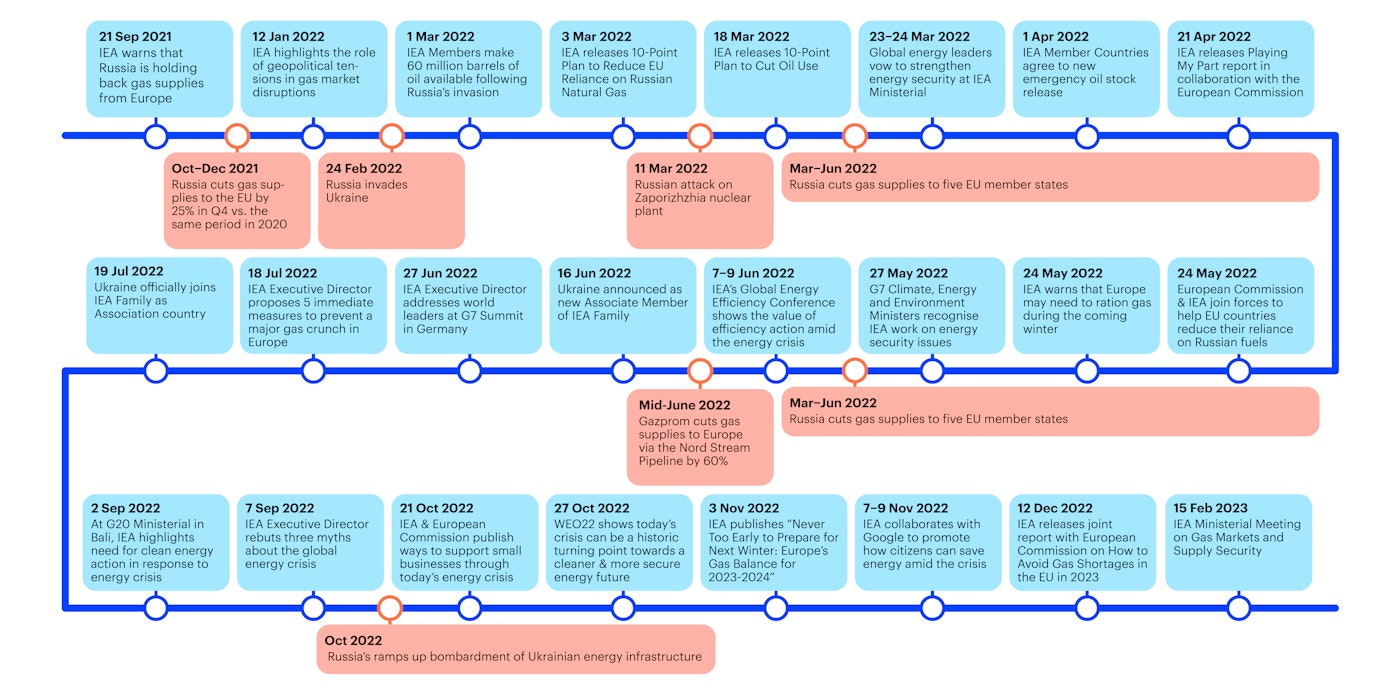
Russia's War on Ukraine
The new energy world
The global energy landscape has changed dramatically
The energy sector continues to feel the effects of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, which in February 2022 sparked the first truly global energy crisis. Two years on, energy prices have pulled back from record highs, but trends vary widely among regions. In many parts of the world, prices are still elevated – holding back economic growth, straining the finances of households and businesses, and complicating efforts to improve access to electricity. Energy markets, faced with an unusually high degree of geopolitical uncertainty, remain on edge.
In Ukraine, the energy sector is on the front line of the war for the second consecutive winter. As temperatures have dropped, Russia has resumed a broad military offensive targeting power plants and other key energy infrastructure across the country, which in 2022 and 2023 caused extensive damage and left many Ukrainians without reliable supplies of electricity or heat for long periods. Recent improvements to Ukraine’s air defence systems have helped safeguard power supply this winter, but Russia’s attacks are ongoing, and additional resources are needed to tackle structural problems that persist within the country’s power sector.
Meanwhile, the war continues to reshape the global energy system in profound ways. Trade patterns for oil and natural gas have shifted dramatically since Russia’s invasion as governments look to strengthen their energy security. At the same time, cleaner alternatives to fossil fuels are growing faster than ever. Due in part to policies unveiled by governments after February 2022, the world’s capacity to produce renewable power is expanding at a remarkable pace, while the popularity of clean technologies such as electric vehicles and heat pumps is surging. The biggest legacy of the global energy crisis triggered by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine may be that it accelerates the end of the fossil fuel era – with IEA projections now showing that under today’s policy settings, demand for oil, gas and coal is set to peak within the decade.
The IEA is partnering with Ukraine as it bolsters its energy security
The IEA and many of our member countries are working closely with Ukraine to help the country’s energy system recover from Russia’s attacks and lay the groundwork for its transition to a secure and sustainable energy future.
The IEA and Ukraine have a long history of collaboration dating back to 2007. In July 2022, Ukraine officially joined the IEA Family as an Association country, and a two-year Joint Work Programme was signed in December 2022. Through the exchange of data, analysis and policy advice, the IEA is supporting Ukraine’s efforts to reconstruct and modernise its energy sector, further integrate its energy system with the European Union’s, and drive down carbon emissions – core objectives outlined in the government’s 2050 energy strategy.
In the past year, the IEA has also convened three workshops with Ukrainian stakeholders, including one in Kyiv. These workshops had a strong focus on the benefits of leveraging distributed energy resources such as solar PV in Ukraine.
With the displacement of people and industry during the war shifting patterns of energy consumption, distributed resources – which have a shorter lead-time for deployment than conventional generation – can help meet demand where it is needed the most. Greater deployment of distributed energy resources would also reduce the power system’s vulnerability to Russian attacks – and could help Ukraine meet its ambition to reduce greenhouse gas emissions 65% by 2030 compared with 1990 levels.
Tracking impacts
Russia remains a top oil exporter, but its revenues have dropped
Russian oil export volumes remained stable year-over-year in 2023 at 7.5 million barrels per day, with a slight loss in crude offset by an equivalent gain in oil products. While overall exports to the European Union, the United States, the United Kingdom and OECD Asia stood at negligible levels, dropping 4.3 million barrels per day below their pre-war average, shipments rose sharply to India, China, Türkiye and countries in the Middle East.
Even so, the monthly average of Russia’s export revenues from commercial oil tumbled in 2023 by USD 4.2 billion year-over-year. This was the result of G7 price caps, increasing discounts for Russian crude and a broader decline in global oil prices.
Average Russian oil exports by country and region, 2021-2023
OpenThe EU has reduced its dependence on Russian gas
After it invaded Ukraine in 2022, Russia cut 80 billion cubic metres (bcm) of pipeline gas supplies to Europe, plunging the region into an energy crisis. While the European Union committed to phase out Russian fossil fuel imports “as soon as possible,” it faced an immediate energy deficit it needed to fill. Due to a slowdown in gas deliveries from Russia’s Gazprom even before the war, as well as unusually weak hydropower and nuclear output, the EU ultimately had to account for 160 bcm of “missing gas” in 2022.
According to IEA analysis, alternative sources of supply – most notably liquefied natural gas (LNG) from the United States – met over 40% of this deficit. However, the main adjustments were on the demand side. Gas use in industry fell by almost 25%, while a mild winter reduced consumption by 10%. New renewable energy capacity and efficiency improvements together lowered gas demand by another 10%. Burning more coal filled less than 4% of the gap.
Natural gas from Russia met less than a quarter of the European Union’s total gas demand in 2022. In 2023, the share declined to roughly 10%, as pipeline deliveries from Russia dropped another 38 bcm and the United States reinforced its position as the EU’s largest LNG supplier.
Share of European Union gas demand met by Russian supply, 2001-2023
OpenThe world’s capacity to generate renewable energy is growing at a record pace
This historic shift comes as governments around the world ramp up support for renewable energy production, seeking to bolster their domestic energy security in the wake of the 2022 crisis while making progress towards climate targets. The Inflation Reduction Act in the United States, the REPowerEU plan in Europe and the GX Green Transformation programme in Japan are just a few examples of the strong action by policymakers taken after Russia’s invasion.
At COP28 in Dubai, nearly 200 governments agreed to triple global renewable energy capacity by 2030, which would take it above 11 000 GW – in line with the IEA’s pathway to build an energy system with net zero emissions by 2050. IEA analysis shows that with stronger policy implementation, that target could be within reach, with capacity currently on track to increase 2.5 times.
Cumulative renewable electricity capacity in the main and accelerated cases and Net Zero Scenario, 2021-2030
OpenKey analysis
IEA's immediate response
The IEA has been at the forefront of managing the global energy crisis that resulted from Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
On two occasions, IEA member countries agreed to take the exceptional step of releasing oil from their emergency reserves to reduce the strains in markets and send a unified message that there would be no shortfall in supplies as a result of Russia’s invasion.
In the first collective action following the invasion, agreed on 1 March 2022, IEA member countries committed to release 62.7 million barrels of emergency oil stocks. On 1 April, they agreed to make a further 120 million barrels available from emergency reserves. This was the largest stock release in the IEA’s history and coincided with the release of additional barrels from the US Strategic Petroleum Reserve. The two coordinated drawdowns in 2022 were the fourth and fifth in the history of the IEA, which was created in 1974. Previous collective actions were taken in 1991, 2005 and 2011.